What is HDD | Hard Disk Drive | Do It Something

What is HDD
What is HDD
If you are familiar with what is HDD you should read this article. Continue reading if you want to learn more about utilizing.
HDD stands for “Hard Disk Drive”. It is a computer device that uses magnetic storage to store and retrieves digital data. Hard disk drives are the most common storage device used in personal computers, laptops, and servers.

They consist of one or more rotating disks or platters coated with a magnetic material and read/write heads that move across the surface of the platters to read or write data. Hard disk drives offer high storage capacities, and relatively fast data transfer rates, and are typically less expensive than other forms of storage such as solid-state drives (SSDs).
Also, Check AirPods Battery Life and Replacement
HDD and SSD Differences

| HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSD (Solid State Drive) |
|---|---|
| Uses spinning disks to store data | Uses memory chips to store data |
| Mechanical parts can cause wear and tear | No mechanical parts, more durable |
| Slower read and write speeds | Faster read and write speeds |
| Larger storage capacity | Smaller storage capacity |
| Heavier and bulkier | Lighter and more compact |
| More affordable | More expensive |
| Suitable for large file storage, e.g. photos, videos, music | Suitable for high-speed data access, e.g. operating systems, applications |
| Generates noise and heat | Generates less noise and heat |
Parts of a Hard Disk Drive
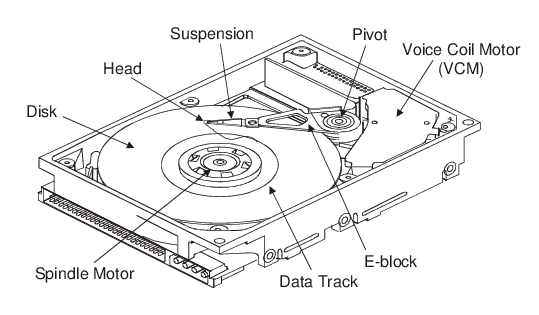
A hard disk drive (HDD) is a type of storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage and spinning disks. The basic parts of a hard disk drive include:
- Platters: These are circular, rotating disks made of glass or aluminum and coated with a magnetic material where data is stored.
- Read/Write Heads: These are small electromechanical devices that read data from and write data to the platters. They float above the platters on a cushion of air created by the spinning platters.
- Actuator Arm: This is the mechanism that moves the read/write heads across the platters to access different areas of the disk.
- Spindle Motor: This is the motor that spins the platters at a constant speed (typically between 5,400 and 7,200 revolutions per minute).
- Controller Board: This is the electronic circuit board that controls the read/write heads, manages data transfer between the drive and the computer, and communicates with the rest of the system.
- Cache: This is a small amount of high-speed memory on the hard drive controller board that stores frequently accessed data for faster access.
- Interface: This is the connector on the hard drive that allows it to communicate with the computer’s motherboard, usually through SATA or IDE interface.
How Data is Stored on a Hard Disk Drive
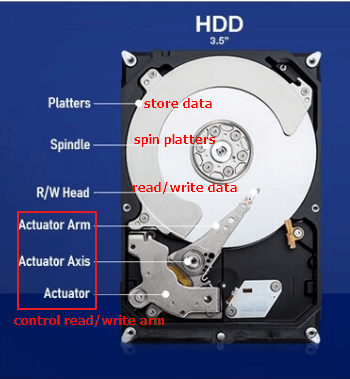
Data is stored on a hard disk drive (HDD) through a process called magnetic recording. The HDD consists of one or more circular platters coated with a magnetic material, and each platter has a read/write head that accesses and stores data on the platter.
When data is written to the HDD, the read/write head modifies the magnetic field of the platter by creating tiny magnetic areas called magnetic domains. These domains are arranged in concentric circles called tracks, which are further divided into sectors.
Also, Read Ranked AI
The read/write head can detect and read the magnetic domains on the platter to retrieve stored data. To write new data, the read/write head aligns itself over the correct track and sector and applies a magnetic field that flips the polarity of the magnetic domains in the targeted sector. This process creates a new pattern of magnetic domains that represent the new data.
To read data, the read/write head moves to the correct track and sector, and reads the magnetic domains to retrieve the stored data. The speed at which data is accessed and retrieved on an HDD depends on the speed at which the platters spin and the speed at which the read/write head can move to the correct position.
Overall, the process of magnetic recording allows for large amounts of data to be stored on an HDD in a relatively small physical space.
Capacity and Speed of Hard Disk Drives

Capacity: The capacity of a hard disk drive is the amount of data that can be stored on the drive. It is typically measured in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB). Over the years, the capacity of hard disk drives has increased significantly, with some drives now offering capacities of up to 20 TB. The amount of capacity you need depends on your storage needs, such as the amount of data you want to store and the type of files you will be working with.
Speed: The speed of a hard disk drive is the rate at which it can read and write data. It is typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). Higher RPMs generally mean faster read and write speeds. For example, a typical laptop hard drive may have an RPM of 5,400, while a faster desktop hard drive may have an RPM of 7,200. However, other factors such as disk density, data transfer rates, and cache size can also impact the speed of a hard drive.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are typically faster than hard disk drives, but they tend to have lower capacities and higher costs. When choosing a hard disk drive, it’s important to consider the balance between capacity and speed that will best meet your needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hard Disk Drives Compared to Other Storage Devices

Advantages of Hard Disk Drives (HDDs):
- Large Storage Capacity: HDDs can store a large amount of data at a relatively low cost compared to other storage devices.
- Durability: Hard disk drives are robust and resistant to wear and tear, making them reliable for long-term use.
- Compatibility: Hard drives are compatible with most computer systems and can be easily swapped between computers.
- Good Read/Write Speeds: HDDs have a reasonable read/write speed, making them suitable for everyday use.
- Cost-Effective: Hard disk drives are cheaper compared to solid-state drives (SSDs), making them a more affordable option for people on a budget.
Disadvantages of Hard Disk Drives (HDDs):
- Slower Performance: Compared to SSDs, HDDs have slower data access and transfer speeds.
- Mechanical Failures: Because of their moving parts, HDDs are prone to mechanical failures, making them vulnerable to physical damage.
- Fragility: Hard drives are vulnerable to damage from shocks and vibrations, which can cause data loss or corruption.
- Energy Consumption: Hard disk drives consume more power compared to other storage devices, leading to higher energy bills.
- Noise and Heat: The spinning platters and moving parts in HDDs can create noise and heat, making them unsuitable for use in noise-sensitive environments.
Maintenance and Care for Hard Disk Drives

Maintaining and caring for your hard disk drive (HDD) is important to ensure that it operates properly and lasts as long as possible. Here are some tips to help you maintain and care for your HDD:
- Keep your HDD clean: Dust and dirt can accumulate on the surface of the HDD, affecting its performance. Use a soft cloth or canned air to clean the exterior of the HDD periodically.
- Avoid extreme temperatures: Hard disk drives are sensitive to temperature changes. Keep your HDD in a location with stable room temperature to prevent overheating or freezing.
- Handle with care: Dropping or jostling your HDD can cause damage to the delicate internal components. Always handle your HDD with care and avoid exposing it to physical shock or impact.
- Defragment your HDD: Over time, data stored on the HDD can become fragmented, causing slower performance. Defragmenting the HDD periodically can help improve performance.
- Use reliable antivirus software: Viruses and malware can cause damage to the HDD and result in data loss. Use reliable antivirus software to protect your HDD and other data storage devices.
- Keep backups: Regularly backing up your data is essential to protect against data loss. Make sure to store your backups in a safe and secure location.
Future of Hard Disk Drives:
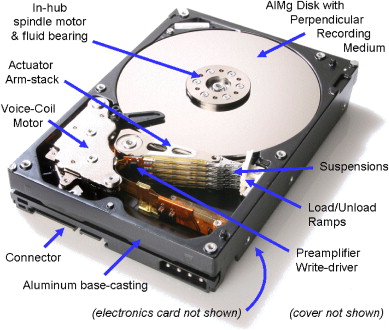
The future of hard disk drives (HDDs) is an interesting topic that has been debated among industry experts and consumers alike. While some believe that HDDs will eventually become obsolete and be replaced by solid-state drives (SSDs), others argue that there is still a place for HDDs in the market.
One potential area for growth in the future of HDDs is their capacity. With the increasing demand for data storage, HDD manufacturers are working to create drives with even larger capacities. In 2021, Western Digital announced a 20TB hard drive, which is currently the largest capacity HDD on the market. However, there is already talk of drives with capacities of up to 50TB in development.
Another area for development is the use of new technologies to increase the speed and reliability of HDDs. For example, manufacturers are exploring the use of heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) and microwave-assisted magnetic recording (MAMR) to increase the density of data storage and reduce the risk of data loss.
Additionally, HDDs may find new applications in the emerging fields of big data and artificial intelligence (AI). With the vast amounts of data generated by these fields, HDDs could provide a cost-effective solution for long-term storage and archival.
Overall, while SSDs have become increasingly popular in recent years, HDDs still have a place in the market and will continue to evolve and improve in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions :
A computer hard disk drive (HDD) is a non-volatile data storage device. Non-volatile refers to storage devices that maintain stored data when turned off. All computers need a storage device, and HDDs are just one example of a type of storage device.
Types of Hard Drives – SATA, PATA, SCSI, and SSD.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are the most common storage drives today. SSDs are smaller and faster than hard disk drives (HDDs). SSDs are noiseless and allow PCs to be thinner and more lightweight. Hard disk drives (HDDs) are more common in older devices.
Conclusion
This was our guide on – What is HDD
A hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a type of storage device used to store and retrieve digital data on a computer or other electronic device. It consists of multiple spinning disks or platters, read/write heads, and an actuator arm that moves the heads over the platters to access data. HDDs use magnetic recording technology to store data and are known for their high capacity and relatively low cost compared to other storage devices.
When considering an HDD, factors such as capacity and speed should be taken into account. While HDDs have advantages such as affordability and durability, they also have some limitations, such as slower speeds compared to solid-state drives and susceptibility to damage from shocks or drops.
Proper maintenance and care can help prolong the life and performance of an HDD. As technology continues to evolve, emerging technologies and trends are shaping the future of hard disk drives. Overall, understanding the basics of HDDs can help users make informed decisions about storage options for their electronic devices.
We hope this article is helpful for you, if you have any queries then comment below.