Microsoft Windows | Do It Something

Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Read this article if you are comfortable with Microsoft Windows. If you want to discover more about utilizing, keep reading.

Microsoft Windows is a family of operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft Corporation. It was first introduced in 1985, and since then, it has become one of the most widely used operating systems in the world, powering millions of devices from desktops and laptops to smartphones and gaming consoles.
Windows is known for its user-friendly interface, customizable settings, and compatibility with a wide range of software and hardware. It has evolved over the years with new versions and updates, introducing new features and improvements.
Some of the popular versions of Windows include Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. Each version has its own unique features and system requirements.
Windows is widely used in various industries, including business, education, healthcare, and entertainment. It is also used by individuals for personal and professional use, making it a versatile operating system for various purposes.
Also, Check What Is Internet Marketing
Versions of Microsoft Windows

| Windows Version | Release Year | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.0 | 1985 | The first release of Windows, basic GUI |
| Windows 2.0 | 1987 | Expanded GUI, support for more applications |
| Windows 3.0 | 1990 | Improved GUI, support for virtual memory, and advanced graphics |
| Windows 95 | 1995 | Taskbar, Start Menu, Plug, and Play support |
| Windows 98 | 1998 | Internet Explorer 4.0, USB support |
| Windows 2000 | 2000 | Active Directory, support for multiple CPUs |
| Windows XP | 2001 | User interface overhaul, improved performance, system restore |
| Windows Vista | 2006 | Aero interface, improved search and security features |
| Windows 7 | 2009 | Faster boot times, improved taskbar and Aero Peek |
| Windows 8 | 2012 | Metro interface, touchscreen support |
| Windows 8.1 | 2013 | Improved Metro interface, Start button |
| Windows 10 | 2015 | Cortana virtual assistant, Edge web browser, Universal apps |
Installing Microsoft Windows
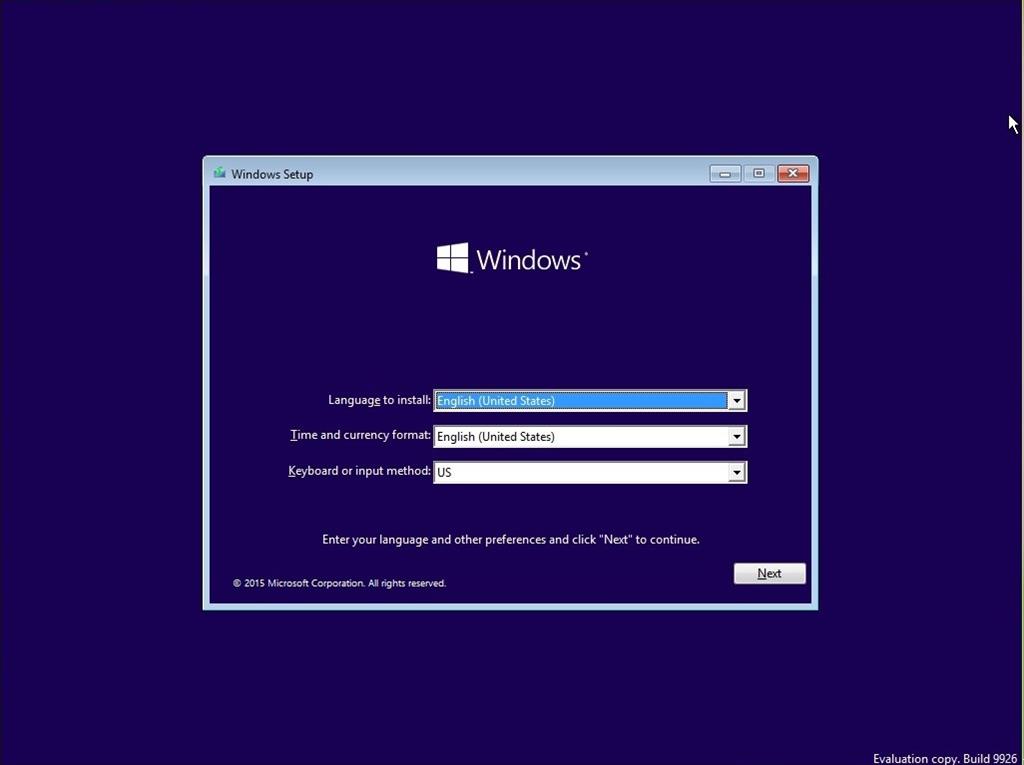
- Get a Windows installation disk or create a bootable USB drive with the Windows installation files.
- Insert the installation disk or plug in the USB drive and restart your computer.
- During startup, enter the BIOS setup by pressing the key (usually F2, F10, or Del) displayed on the screen.
- In the BIOS setup, change the boot order to prioritize the installation disk or USB drive.
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS setup.
- The Windows installation screen will appear. Select your language, time and currency format, and keyboard layout, and then click Next.
- Click Install Now and enter the product key when prompted.
- Read and accept the license terms, and then click Next.
- Choose the type of installation you want and follow the prompts to select the drive where you want to install Windows.
- The installation process will start and may take several minutes to complete. Your computer will restart several times during the installation process.
- Once the installation is complete, you will be prompted to create a user account and set up Windows settings.
- Follow the prompts to complete the setup and personalize your Windows installation.
The Windows Desktop and Start Menu
The Windows Desktop and Start Menu are two of the most important elements of the Microsoft Windows operating system. Here’s an overview of each:
Also, read What Is Leadbit Affiliate Network
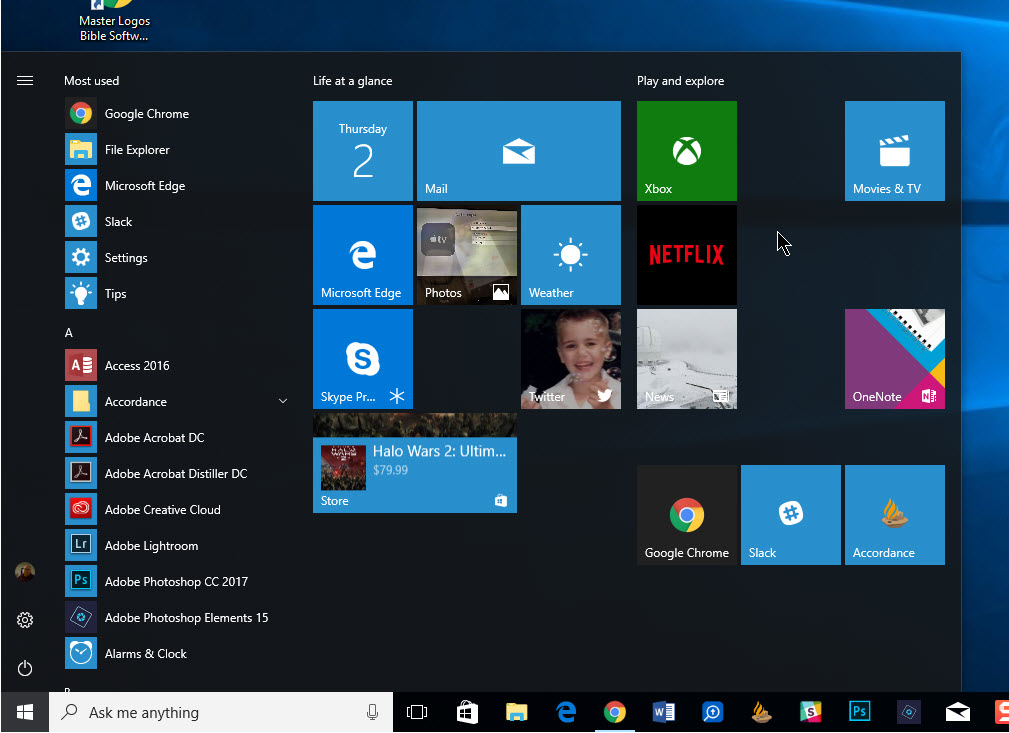
- Windows Desktop: The desktop is the main screen you see when you start your computer. It serves as a workspace where you can arrange and access your files, folders, and shortcuts. The Windows desktop includes a taskbar at the bottom of the screen, which displays running applications and system notifications, as well as an area where you can place shortcuts to your favorite programs and files.
- Start Menu: The Start menu is the central hub for accessing programs, settings, and files in Windows. It can be accessed by clicking on the Windows icon located at the bottom-left corner of the desktop, or by pressing the Windows key on your keyboard. The Start menu includes a list of frequently used apps and recently added programs, as well as shortcuts to various system tools and settings. In Windows 10, the Start menu also includes live tiles, which display real-time information from your favorite apps.
Both the desktop and Start menu can be customized to suit your preferences. You can change the desktop background, adjust the taskbar settings, and add or remove shortcuts from the desktop. Similarly, you can customize the Start menu by pinning frequently used apps, resizing the menu, and organizing apps into folders.
Managing Files and Folders in Windows
Managing files and folders is an essential part of using Microsoft Windows. Here are some subheadings related to this topic:
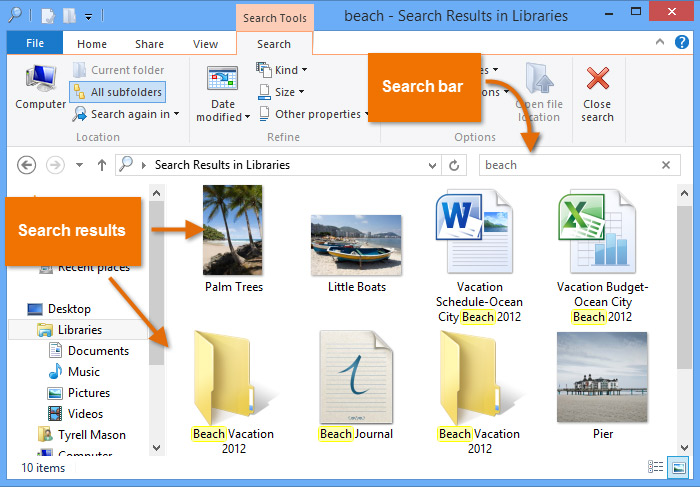
- Understanding File Systems in Windows
- Navigating the File Explorer
- Creating and Renaming Files and Folders
- Moving and Copying Files and Folders
- Deleting and Restoring Files and Folders
- Managing File and Folder Permissions
- Searching for Files and Folders
- Using Libraries in Windows
- Using Cloud Storage Services with Windows
- Organizing Files and Folders with File Explorer Options.
Customizing Windows Settings
Customizing Windows Settings allows you to personalize your experience with the operating system. Here are some areas where you can customize settings in Microsoft Windows:

- Personalization: Change the background, colors, and theme of your Windows desktop.
- Display: Adjust the resolution, scaling, and orientation of your display.
- Sound: Change the sound scheme, adjust the volume, and configure audio devices.
- Notifications and actions: Customize the notification settings and which notifications you receive.
- Apps: Configure default apps, app permissions, and app settings.
- Devices: Manage and customize settings for your connected devices such as printers and scanners.
- Power and sleep: Configure settings for power management and sleep mode.
- Privacy: Customize your privacy settings and choose which apps have access to your data.
- Update and security: Configure settings for updates, security, and backup.
- Accessibility: Customize settings for accessibility options such as visual, hearing, and mobility impairments.
Installing and Managing Programs in Windows
Great choice! Here are some possible subheadings for installing and managing programs in Microsoft Windows:

- Installing Programs in Windows
- Finding and Downloading Software for Windows
- Installing Software from Physical Media
- Managing Installed Programs in Windows
- Updating Software in Windows
- Uninstalling Programs in Windows
- Managing Startup Programs in Windows
- Running Programs in Compatibility Mode
- Troubleshooting Program Installation Issues in Windows
- Using Windows Store to Install and Manage Apps
- Managing Default Programs in Windows.
Troubleshooting Windows Issues
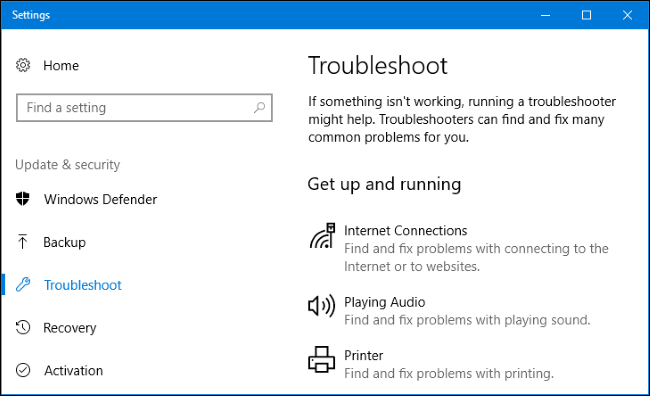
- Blue Screen of Death (BSOD): This is a critical system error that can cause your computer to shut down. To troubleshoot this issue, try restarting your computer and see if the problem persists. If it does, you may need to restore your system to a previous point or reinstall Windows.
- Slow Performance: If your computer is running slowly, it may be due to low disk space, too many programs running at once, or a virus/malware infection. You can troubleshoot this issue by running a virus scan, deleting unnecessary files, and disabling unnecessary startup programs.
- Windows Updates: Sometimes, Windows updates can cause problems with your computer, such as crashes or freezes. To troubleshoot this issue, you can try restarting your computer, checking for new updates, and rolling back any recent updates.
- Driver Issues: If your hardware devices are not working correctly, it may be due to outdated or corrupted drivers. You can troubleshoot this issue by updating your drivers or rolling them back to a previous version.
- Internet Connection Problems: If you are having trouble connecting to the internet, you can troubleshoot this issue by checking your network settings, resetting your router/modem, or contacting your internet service provider.
- Application Compatibility Issues: If an application is not running correctly on your Windows computer, it may be due to compatibility issues with your operating system. You can troubleshoot this issue by running the application in compatibility mode or updating it to a newer version.
These are just a few examples of Windows issues and troubleshooting steps. If you continue to experience problems with your Windows computer, it may be helpful to consult with a professional or seek support from Microsoft.
Windows Security and Privacy
- Overview of Windows Security Features
- Configuring User Accounts and Passwords
- Windows Firewall and Network Security
- Windows Defender and Antivirus Protection
- Encrypting Files and Folders in Windows
- Internet Security and Privacy Settings in Windows
- Configuring Windows Updates for Security
- Using Windows Event Viewer for Security Monitoring
- Protecting Your Online Identity in Windows
- Best Practices for Windows Security and Privacy.
Networking with Windows
Networking with Windows is a crucial aspect of using the operating system in a business or home environment. Here are some subheadings related to networking with Windows:
- Setting up a Local Area Network (LAN)
- Configuring Network Settings in Windows
- Sharing Files and Printers on a Network
- Joining a Domain or Workgroup
- Remote Desktop and Remote Assistance
- Configuring Windows Firewall for Networking
- Wireless Networking with Windows
- Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues
- VPN and Remote Access in Windows
- Network Security and Permissions in Windows.
Microsoft Windows Tips and Tricks.
Certainly! Here are some tips and tricks for Microsoft Windows:

- Use keyboard shortcuts: Windows has a lot of keyboard shortcuts that can help you navigate and use the operating system more efficiently. Some common ones include Ctrl+C (copy), Ctrl+V (paste), and Ctrl+Z (undo).
- Customize the Start Menu: You can customize the Start Menu by pinning your favorite apps and programs to it. Simply right-click on an app or program and select “Pin to Start”.
- Use Virtual Desktops: If you find yourself with a lot of open windows, you can use virtual desktops to organize them. Simply press Windows+Tab and then click “New Desktop” to create a new virtual desktop.
- Search for files and programs: Instead of manually searching through your files and programs, you can use the Windows Search feature. Simply click on the Start Menu and start typing what you’re looking for.
- Use Task Manager: If an app or program is not responding or causing problems, you can use the Task Manager to force quit it. Simply press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open Task Manager.
Also, read
- Change the size of text and apps: If the text or apps on your screen are too small or too big, you can change the size in the Display Settings. Simply right-click on the desktop and select “Display Settings”.
- Use the Snipping Tool: If you need to take a screenshot of something on your screen, you can use the Snipping Tool. Simply search for “Snipping Tool” in the Start Menu and open it.
- Use Windows Update: It’s important to keep your operating system up-to-date to ensure that it’s secure and running smoothly. You can use Windows Update to download and install the latest updates.
- Customize the Taskbar: You can customize the Taskbar by adding or removing icons and changing their position. Simply right-click on the Taskbar and select “Taskbar settings”.
- Use Cortana: Cortana is Windows’ virtual assistant that can help you with tasks like setting reminders, finding files, and answering questions. Simply click on the search bar and start typing your question or command.
Frequently Asked Questions :
For example, you can use Windows to browse the Internet, check your email, edit digital photos, listen to music, play games, and do much more. Windows is also used in many offices because it gives you access to productivity tools such as calendars, word processors, and spreadsheets.
Windows 11 is the latest major release of Microsoft’s Windows NT operating system, released in October 2021.
Major features include- the start menu, task manager, taskbar, Cortana, file explorer, MS Paint, Browser, control panel, etc. The advantages of the windows Operating system are- the majority of the users use Windows, it has programming and gaming support, clean and lucid GUI, and Microsoft Office support.
Conclusion
This was our guide on – Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a popular operating system used by millions of people around the world. It offers a wide range of features and capabilities that allow users to customize their experience and work efficiently.
By using tips and tricks like keyboard shortcuts, customizing the Start Menu, and using virtual desktops, users can further enhance their productivity and efficiency. It’s important to keep Windows up-to-date and use tools like Task Manager and Windows Update to ensure the system is running smoothly and securely.
With its user-friendly interface and wide range of capabilities, Microsoft Windows remains a top choice for users across the globe.
We sincerely hope that this essay has enlightened you on Microsoft Windows. Please let us know in the comments area if you have any questions.
This article is recommended reading if you are familiar with Microsoft Windows. If you’re interested in finding out more about utilizing, keep reading.







