Best Computer Network [2023] Do It Something

Best Computer network
Computer Network
Did you know about Computer network, if yes then this article is for you. We will be discussing. Read on for more
A computer network is a collection of interconnected devices, such as computers, printers, servers, routers, and switches, that can communicate with each other and share resources such as data, applications, and devices.
Networks can be categorised into different types based on their geographical range, such as Local Area Networks (LANs) that cover a small area, such as a home or office building, and Wide Area Networks (WANs) that cover a larger geographical area, such as a city, country, or even the entire world.

Networks can also be categorized based on their topology, or the way in which devices are interconnected. Common topologies include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree.
Computer networks rely on various communication protocols and technologies to allow devices to communicate with each other and share resources. These include wired and wireless communication technologies, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, as well as protocols such as TCP/IP, HTTP, and DNS.
How Does a Computer Network Work?
A computer network works by allowing devices connected to the network to communicate and share resources. Here’s how it works:
- Devices on the network are connected through wired or wireless connections. Wired connections typically use Ethernet cables, while wireless connections use Wi-Fi.
- Each device on the network has a unique identifier, known as an IP address. This allows devices to communicate with each other using network protocols such as TCP/IP.
- Data is transmitted between devices in the form of packets. These packets contain the data being transmitted, as well as addressing and error-checking information.
- Network devices such as routers and switches direct data packets to their intended destinations on the network.
- Network services such as file sharing, printing, and internet access are made available to devices on the network through the use of network software and protocols.
- Network security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and access control are used to protect the network from unauthorised access, data breaches, and other threats.
Omit computer network is a complex system that involves the interconnection of hardware, software, and protocols to enable communication and resource sharing between devices on the network.
Also read about E-Commerce Affiliate Network
Basic Terminologies of Computer Networks table below
Sure, here is a table of basic terminologies used in computer networks:
| Terminology | Definition |
| Protocol | A set of rules that governs the communication between devices on a network. |
| IP address | A unique numerical identifier assigned to each device on a network. |
| Router | A device that directs traffic between different networks. |
| Switch | A device that connects multiple devices within a network and forwards data between them. |
| Hub | A device that connects multiple devices within a network and broadcasts data to all connected devices. |
| Firewall | A security device that blocks unauthorized access to a network. |
| DNS (Domain Name System) | A system that translates domain names into IP addresses. |
| LAN (Local Area Network) | A network that covers a small area, such as a home or office. |
| WAN (Wide Area Network) | A network that covers a large geographical area, such as a city or country. |
| VPN (Virtual Private Network) | A secure connection between two networks or devices over a public network, such as the internet. |
| Bandwidth | The amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time. |
| Latency | The amount of time it takes for data to travel between two devices on a network. |
| Ethernet | A standard for wired network connections. |
| Wi-Fi | A wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to connect devices to a network. |
| MAC address | A unique identifier assigned to each network interface card (NIC) on a device. |
Types of Enterprise Computer Networks
There are several types of enterprise computer networks, each designed to meet different business needs. Here are some of the most common types of enterprise networks:
- Local Area Network (LAN) – A LAN is a network that connects devices within a small geographic area, such as a single building or campus. It is typically used to help communication and data sharing among employees within an organization.
- Wide Area Network (WAN) – A WAN is a network that connects devices over a larger geographic area, such as many buildings, cities, or even countries. It is typically used to connect many LANs together and to provide access to the internet.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) – A VPN is a secure network that connects devices over a public network, such as the internet. It is typically used to provide remote access to corporate resources for employees who are working outside of the office.
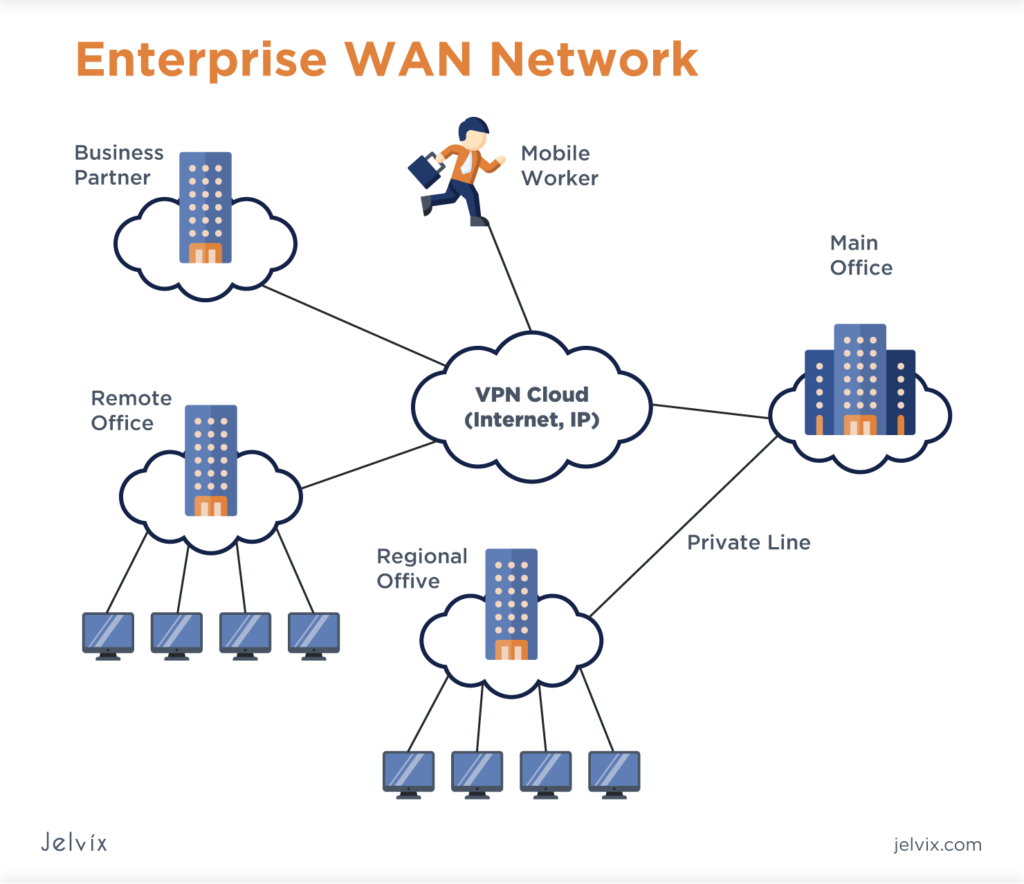
- Storage Area Network (SAN) – A SAN is a specialized network that provides high-speed access to storage devices such as disks and tapes. It is typically used to support large data storage requirements and data-intensive applications such as video streaming and database management.
- Wireless Network – A wireless network is a LAN or WAN that uses wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi to connect devices. It is typically used to provide mobile access to corporate resources and to enable flexible and mobile work environments.
These are just a few examples of the types of enterprise computer networks. Each network has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of network type will depend on the specific needs of the organization
Types of Computer Network Architecture
- Client-Server Architecture – This is the most common type of network architecture. In this architecture, one or more servers provide services to many clients on the network. Clients access the server(s) to perform tasks such as file sharing, printing, email, and database access. The server manages the resources and responds to client requests.
- Peer-to-Peer Architecture – In this architecture, all devices on the network are equal and can act as both a client and a server. Each device can share its resources, such as files or printers, with other devices on the network. Peer-to-peer networks are commonly used in small networks or workgroups.
- Centralized Architecture – In this architecture, all resources are located in a central location, such as a mainframe or a server. Clients connect to the central location to access the resources they need. This architecture provides centralized control and management of resources.
- Distributed Architecture – In this architecture, resources are distributed across the network, and clients access the resources from the closest available source. This architecture provides better performance and redundancy than centralised architecture, as resources can be located closer to the clients who need them.
- Hybrid Architecture – This architecture combines two or more of the above architectures to meet the specific needs of the organisation. For example, an organisation may use a client-server architecture for its internal network and a cloud architecture for its public-facing services.
Network Topology
- Bus Topology – In this topology, all devices are connected to a single cable, which is known as the backbone. Data is transmitted in both directions along the backbone. The advantage of a bus topology is that it is easy to set up and requires less cabling than other topologies. But, it can be difficult to troubleshoot and scale.
- Star Topology – In this topology, all devices are connected to a central device, such as a switch or hub. Data is transmitted through the central device to the intended recipient. The advantage of a star topology is that it is easy to troubleshoot and scale. But, it requires more cabling than a bus topology and can be more expensive to set up.
- Ring Topology – In this topology, devices are connected in a closed loop, with data transmitted in one direction around the ring. Each device acts as a repeater, regenerating and passing on the signal. The advantage of a ring topology is that it is efficient and can support a large number of devices. But, it can be difficult to troubleshoot and scale.

- Tree Topology – In this topology, devices are arranged in a hierarchical structure, with branches branching off from a central trunk. Data is transmitted up and down the tree, with each branch connecting to a central node. The advantage of a tree topology is that it is scalable and can support a large number of devices. But, it can be difficult to troubleshoot and can be vulnerable to single points of failure.
OSI Model
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework for understanding how network communication occurs between devices. The model is divided into seven layers, each of which performs a specific function in the communication process. The layers are:
- Physical Layer – This layer handles the transmission and reception of raw bit streams over a physical medium, such as a cable or wireless signal.
- Data Link Layer – This layer handles the reliable transmission of data over a physical link between two devices, such as a switch and a computer.
- Network Layer – This layer handles the routing and delivery of data between networks. It determines the best path for data to travel between different networks and manages network traffic.
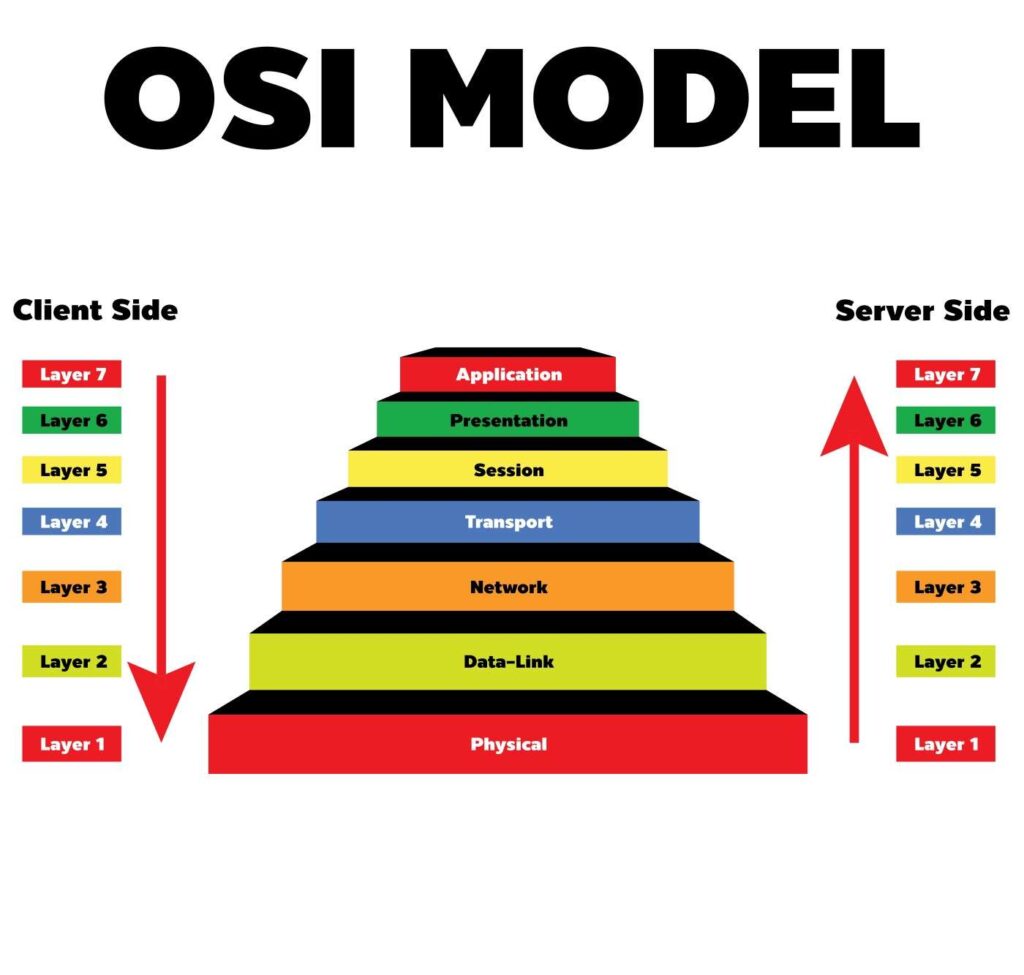
- Transport Layer – This layer handles the reliable transmission of data between devices, including error detection and correction. It ensures that data is delivered in the correct order and without loss or duplication.
- Session Layer – This layer handles establishing and maintaining connections between devices, including the management of data exchange and synchronisation.
- Presentation Layer – This layer handles the conversion of data into a format that can be understood by the receiving device. It deals with issues such as encryption, compression, and data formatting.
- Application Layer – This layer handles providing services to the user, such as email, file transfer, and web browsing. It interacts directly with the user and provides a means of accessing network resources.
The OSI model provides a framework for understanding the different functions of network communication and how they interact with each other. Each layer is designed to perform a specific function, and communication between layers is standardised to ensure compatibility between different devices and networks.
Unique Identifiers of Network
Unique identifiers are used in networks to identify individual devices and ensure that data is sent to the correct destination. Here are some examples of unique identifiers used in networks:
- MAC Address – A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in communications within a network segment. It is a 48-bit number and is typically represented in hexadecimal notation. MAC addresses are used at the data link layer of the OSI model.
- IP Address – An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifier assigned to every device on a network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It is a 32-bit or 128-bit number and is typically represented in decimal notation. IP addresses are used at the network layer of the OSI model.
- Port Number – A port number is a 16-bit number used to identify a specific process or application running on a device. Ports are used to distinguish between different network services running on the same device. For example, port 80 is used for HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) traffic, while port 443 is used for HTTPS (HTTP Secure) traffic.
Read more article 12 Unique Business Ideas
Frequently Asked Questions :
Computer networking refers to interconnected computing devices that can exchange data and share resources with each other. These networked devices use a system of rules, called communications protocols, to transmit information over physical or wireless technologies.
Below mentioned are different types of networks: PAN (Personal Area Network) LAN (Local Area Network) MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) WAN (Wide Area Network)
Computer networks enable communication for every business, entertainment, and research purpose. The internet, online search, email, audio and video sharing, online commerce, live-streaming, and social networks all exist because of computer networks.
Conclusion
Computers, printers, servers, routers, and switches are examples of networked devices that may talk with one another and share resources including data, software, and hardware.
Local Area Networks (LANs), which cover a smaller region, such as a home or office building, and Wide Area Networks (WANs), which cover a wider geographic area, such as a city, country, or even the entire world, are two different types of networks.
We hope that this article has helped you to know about Computer network. If you have any questions, kindly let us know in the comments section







