Joint-stock company Review [2023] Do It Something

Joint-stock company
Joint-stock company
Did you know about the Joint-stock company, If yes then this article is for you. We will be discussing. Read on for more.
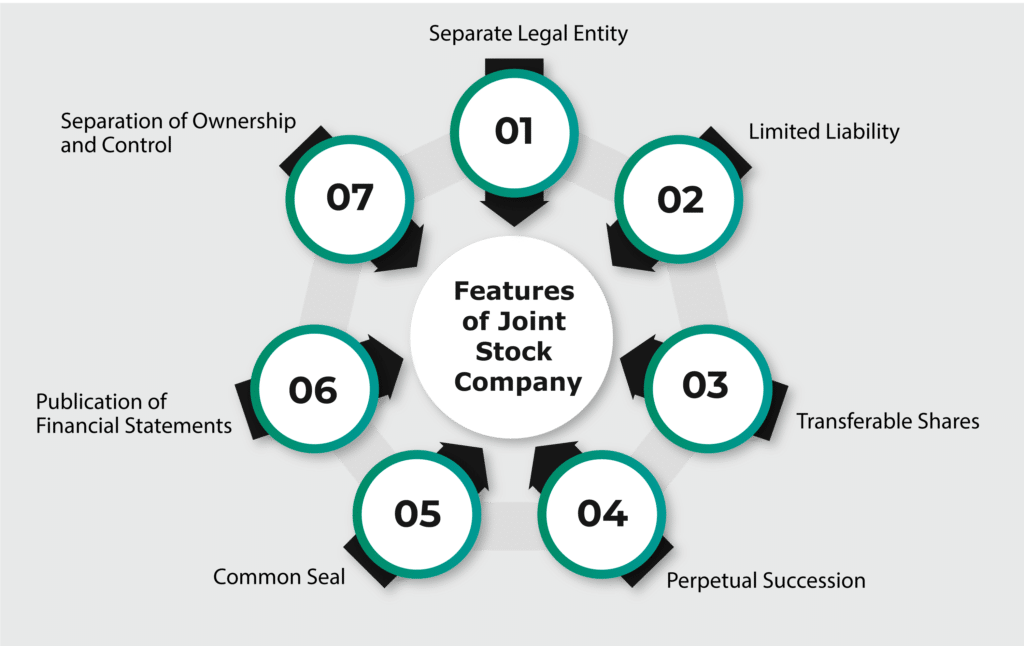
A joint-stock company, also known as a corporation, is a type of business organization that is owned by shareholders.
It is a legal entity that is separate from its owners, and it can enter into contracts, borrow money, and sue or be sued in its own name.
The shareholders of a invest their money by buying shares in the. Each share represents a part of ownership in the company, and shareholders are entitled to a share of the company’s profits in the form of dividends.
They also have the right to vote on important company decisions, such as the election of the board of directors.

One of the main advantages of a is that it allows for the pooling of resources from many investors, which can help to raise large amounts of capital for the business.
It also provides a degree of limited liability for shareholders, which means that their personal assets are protected from the company’s debts and liabilities.
But, joint-stock companies are also subject to a range of legal and regulatory requirements, including the need to file annual reports, hold shareholder meetings, and follow various corporate governance rules.
What is Joint-stock company
It is an entity in which the capital is divided into parts or shares that can be traded on the stock exchange.
The shareholders of a contribute capital to the company in exchange for ownership in the form of shares. The number of shares a shareholder owns represents their proportional ownership in the company. Shareholders can vote on important company decisions, such as the election of the board of directors and major business decisions.
The main advantage of a joint-stock company is that it allows for the pooling of resources from many investors, which can help raise large amounts of capital for the business. Also, the company has a legal identity separate from its owners, which provides limited liability protection to shareholders. This means that their personal assets are not at risk if the company runs into financial trouble.
Joint-stock companies are subject to various legal and regulatory requirements, including the need to file annual reports, hold shareholder meetings, and follow corporate governance rules. They are also typically taxed differently from other types of businesses, such as partnerships or sole proprietorships.
Explained
Sure! Here are some key takeaways on Joint-Stock Company:
- A joint-stock company is a type of business organization where the ownership is divided into shares that are owned by shareholders.
- Shareholders of a invest their money by buying shares in the company. Each share represents a part of ownership in the company, and shareholders are entitled to a share of the company’s profits in the form of dividends.
- One of the main advantages of a joint-stock company is that it allows for the pooling of resources from many investors, which can help raise large amounts of capital for the business.

- Joint-stock companies are also subject to a range of legal and regulatory requirements, including the need to file annual reports, hold shareholder meetings, and follow various corporate governance rules.
- The company has a legal identity separate from its owners, which provides limited liability protection to shareholders. This means that their personal assets are not at risk if the company runs into financial trouble.
- Joint-stock companies are taxed differently from other types of businesses, such as partnerships or sole proprietorships.
- The shareholders can vote on important company decisions, such as the election of the board of directors and major business decisions.
- Joint-stock companies can issue different types of shares, such as common shares and preferred shares, each with different rights and benefits.
- Joint-stock companies can be publicly traded on a stock exchange, which allows the company to raise more capital by selling shares to the public.
Definition
The shareholders of a joint-stock company invest their money by buying shares in the company. Each share represents a part of ownership in the company, and shareholders are entitled to a share of the company’s profits in the form of dividends.
They also have the right to vote on important company decisions, such as the election of the board of directors. The company has a legal identity separate from its owners, which provides limited liability protection to shareholders.
This means that their personal assets are not at risk if the company runs into financial trouble. Joint-stock companies are subject to various legal and regulatory requirements, including the need to file annual reports, hold shareholder meetings, and follow corporate governance rules.
Joint-Stock Company Features
Sure! Here are some features of Joint-Stock Company:
- Transferable Shares: The ownership of a joint-stock company is represented by shares, which are freely transferable. Shareholders can buy and sell shares without the need for the company’s permission.
- Perpetual Succession: Joint-stock companies have perpetual succession, which means that the company can continue to exist even if shareholders die or sell their shares.
- Professional Management: Joint-stock companies have a professional management structure, which handles day-to-day operations of the company. Shareholders elect a board of directors to oversee the management and make strategic decisions.
- Separation of Ownership and Management: Joint-stock companies have a separation of ownership and management. Shareholders own the company but do not manage its operations, while the management team runs the company but does not own it.
- Ability to Raise Capital: Joint-stock companies can raise large amounts of capital by issuing shares to the public. This allows the company to finance its operations and investments without incurring debt.
Examples
There are many examples of joint-stock companies around the world. Here are a few well-known examples:
- Apple Inc.: Apple is a joint-stock company headquartered in California, USA. It designs, develops, and sells consumer electronics, computer software, and online services.
- Coca-Cola Company: Coca-Cola is a joint-stock company headquartered in Georgia, USA. It is a global beverage company that produces and sells soft drinks, juices, and other non-alcoholic beverages.
- Volkswagen AG: Volkswagen is a joint-stock company headquartered in Wolfsburg, Germany. It is one of the world’s largest automotive companies, producing and selling cars, trucks, and buses under various brands, including Volkswagen, Audi, Porsche, and Skoda.
- Royal Dutch Shell plc: Royal Dutch Shell is a joint-stock company headquartered in The Hague, Netherlands. It is one of the world’s largest oil and gas companies, engaged in the exploration, production, refining, and marketing of petroleum products.
- Toyota Motor Corporation: Toyota is a joint-stock company headquartered in Toyota City, Japan. It is one of the world’s largest automotive companies, producing and selling cars, trucks, and buses under various brands, including Toyota, Lexus, and Hino.
These are just a few examples of the many joint-stock companies that exist around the world.
Also read about Top 10 SEO Tools
Types of Joint Stock Companies
There are several types of joint-stock companies, each with its unique characteristics and legal requirements. Here are some common types of joint-stock companies:
- Public Joint-Stock Company: A public joint-stock company is a company whose shares are publicly traded on a stock exchange. It is required to have a least number of shareholders and meet other regulatory requirements, such as filing periodic financial reports.
- Listed Joint-Stock Company: A listed joint-stock company is a company whose shares are listed on a stock exchange. It must meet the regulatory requirements of the stock exchange, including filing periodic financial reports.
- Non-Listed Joint-Stock Company: A non-listed joint-stock company is a company whose shares are not listed on a stock exchange. It is not required to meet the same regulatory requirements as a listed joint-stock company.
- Close Joint-Stock Company: A close joint-stock company is a company whose shares are held by a small group of individuals, and the shares cannot be transferred to the public. It is not required to meet the same regulatory requirements as a public joint-stock company.
These are just a few common types of joint-stock companies. The specific legal requirements for each type may vary depending on the country and jurisdiction where the company is incorporated.
Disadvantages
While there are many advantages to forming a joint-stock company, there are also some disadvantages to consider. Here are some common disadvantages:
- Complex Legal Requirements: Joint-stock companies are subject to complex legal requirements, such as registration, reporting, and compliance with regulations. This can be time-consuming and expensive.

- Lack of Control: Shareholders in a joint-stock company have limited control over the company’s management and operations. This can be frustrating for minority shareholders who may not agree with the decisions of the majority shareholders.
- Shareholder Conflicts: Shareholders in a joint-stock company may have conflicting interests, which can lead to disputes and conflicts. This can be particularly challenging in large public joint-stock companies with many shareholders.
- Costly to Establish: Forming a joint-stock company can be expensive, particularly omit legal and accounting fees.
- Public Disclosure: Public joint-stock companies are required to disclose financial information to the public. Which can be disadvantageous if the company is not performing well or has other negative news.
These are just a few of the potential disadvantages of forming a joint-stock company. It’s important to carefully consider the pros and cons and seek professional advice before deciding to form a joint-stock company.
Also read about What Is Half-Life 2
Frequently Asked Questions :
Entirely Separate Legal Entity: A Joint-Stock Company, in contrast to a partnership or a proprietorship firm, is legally distinct from its owners. It is a separate legal entity from the rest of the organisation. A Company’s activities are not liable for the actions of any one of its members.
The primary objective of Joint Stock Companies is to significantly increase the amount of investment received by corporations.
Economic development: Joint Stock Companies have large financial resources, they are able to undertake large-scale production, satisfy the needs of more consumers, create large-scale employment opportunities, promote balanced regional development and contribute substantially to the government by way of taxes.
Conclusion
A joint-stock company, also known as a corporation, is a type of business organization that is owned by shareholders.
It is a legal entity that is separate from its owners, and it can enter into contracts, borrow money, and sue or be sued in its own name.
The shareholders of a joint-stock company invest their money by buying shares in the company. Each share represents a part of ownership in the company.
Shareholders are entitled to a share of the company’s profits in the form of dividends.
We hope that this article will help you to get a better perception of the Joint-stock company meaning and how it affects your life. We will update this post as soon as possible