What Is Cryptographic Key | 2023] Do It Something

Cryptographic Key
Cryptographic Key
Did you know about if yes then this article is for you. We will be discussing Cryptographic Key. Read on for more.
A cryptographic key is a piece of information used to encrypt or decrypt data in a cryptographic system. It is essentially a secret code or password that is used to secure information and ensure that only authorized parties can access it.

In symmetric-key cryptography, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, and both parties must have access to the same key to communicate securely. In contrast, in public-key cryptography, there are two keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt data, while the private key is used to decrypt it. This enables secure communication even if the parties have not before shared a secret key.
Cryptographic keys are typically generated using algorithms that are designed to produce keys that are highly random and so difficult to guess or predict. They are usually of a fixed length, and longer keys are generally considered more secure than shorter ones.
The security of a cryptographic system depends on the secrecy and randomness of the keys used. If an attacker is able to guess or get a key, they can potentially access sensitive information or even break the entire system. So, the protection and management of cryptographic keys is a critical aspect of information security.
What is Cryptographic Key
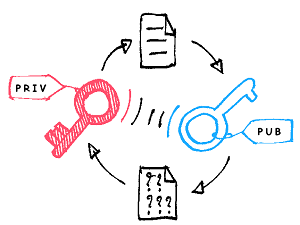
A cryptographic key is a piece of information that is used to secure data in a cryptographic system. It is essentially a secret code or password that is used to encrypt or decrypt data, and ensures that only authorised parties can access it.
In symmetric-key cryptography, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, and both parties must have access to the same key to communicate securely. In contrast, in public-key cryptography, there are two keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt data, while the private key is used to decrypt it. This enables secure communication even if the parties have not before shared a secret key.
Cryptographic keys are typically generated using algorithms that are designed to produce keys that are highly random and so difficult to guess or predict. They are usually of a fixed length, and longer keys are generally considered more secure than shorter ones.
The security of a cryptographic system depends on the secrecy and randomness of the keys used. If an attacker is able to guess or get a key, they can potentially access sensitive information or even break the entire system. so, the protection and management of cryptographic keys is a critical aspect of information security.
What is “Secret Key Cryptography”?
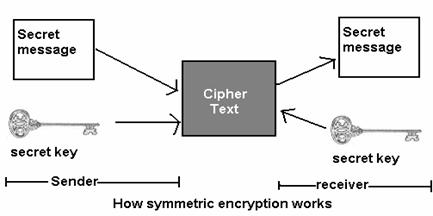
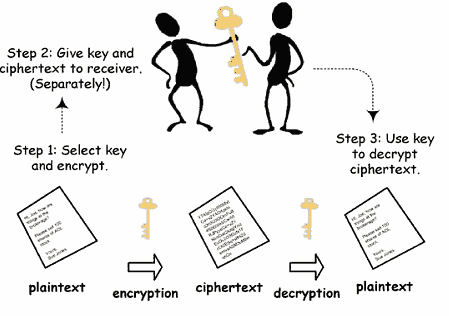
Secret Key Cryptography, also known as Symmetric Key Cryptography, is a type of cryptographic system in which the same secret key is used both for encryption and decryption of the data. The sender and receiver of the message must both have the same secret key to be able to communicate securely.
In secret key cryptography, the plaintext (unencrypted data) is transformed using an encryption algorithm and the secret key, resulting in the ciphertext (encrypted data). The same secret key is used to decrypt the ciphertext back to plaintext.
Secret key cryptography is typically faster and more efficient than public key cryptography, making it a popular choice for secure communication over a network or the internet. But, it can be less secure than public key cryptography since the secret key must be shared between both parties. If the secret key is compromised, all communication between the parties can be read and modified by attackers.
To maintain security, secret key cryptography requires secure distribution and storage of the secret key, and the use of secure algorithms to prevent unauthorised access and tampering. Common examples of secret key cryptography algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), and Blowfish.
Why do we use Secret Key Cryptography?
We use Secret Key Cryptography, also known as Symmetric Key Cryptography, for several reasons:
- Confidentiality: Secret key cryptography provides confidentiality by encrypting the data using a secret key that only the sender and receiver have. This ensures that only authorised parties can access the data and protects it from unauthorised access.
- Efficiency: Secret key cryptography is generally faster and more efficient than public key cryptography, making it ideal for situations where speed is important, such as encrypting large amounts of data.
- Security: Secret key cryptography algorithms are designed to be secure and resist attacks from unauthorised parties. When used properly, secret key cryptography can provide a high level of security for encrypted data.
- Compatibility: Secret key cryptography is widely used and supported by most cryptographic software and hardware, making it a reliable and compatible option for secure communication.
But, there are some limitations to secret key cryptography. The main limitation is that the same secret key must be shared between both parties, which can be difficult to manage securely. Additionally, secret key cryptography does not provide authentication or non-repudiation, which are important security features for certain types of communication. so, in some situations, public key cryptography may be a better choice.
What is the difference between public-key and secret-key cryptography?
Here is a table summarizing some of the main differences between public-key and secret-key cryptography:
| Public-Key Cryptography | Secret Key Cryptography |
| Uses two keys (public and private) for encryption and decryption | Uses a single key for encryption and decryption |
| The public key can be freely shared with anyone | The secret key must be kept secret and shared between parties |
| Offers key exchange and digital signatures | Does not offer key exchange or digital signatures |
| Slower and less efficient than secret key cryptography | Faster and more efficient than public key cryptography |
| More secure for key exchange and when key management is difficult | Less secure for key exchange and when key management is difficult |
It’s worth noting that both types of cryptography have their strengths and weaknesses and are used for different purposes depending on the specific needs of the system. Public-key cryptography is commonly used for secure communication over a network or the internet, while secret key cryptography is used for encrypting large amounts of data or when speed and efficiency are important.
Future of Cryptography
The future of cryptography is an area of ongoing research and development, with new advancements and techniques emerging all the time. Here are some potential directions that cryptography may take in the future:
- Quantum Cryptography: Quantum cryptography is a type of cryptography that relies on the principles of quantum mechanics to secure communication. It has the potential to provide unparalleled security against eavesdropping and attacks from quantum computers. But, current quantum cryptography technologies are still in the experimental phase and have some practical limitations.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: As quantum computing technology advances, it could potentially break many of the encryption schemes that are currently in use. Post-quantum cryptography is an area of research that focuses on developing new encryption schemes that would be resistant to attacks from quantum computers.

- Homomorphic Encryption: Homomorphic encryption is a technique that allows computation to be performed on encrypted data without requiring the data to be decrypted first. This could be a game-changer for secure computation in cloud computing and other applications where privacy is important.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Zero-knowledge proofs are a cryptographic technique that allows a party to prove that they know a secret without revealing any information about the secret itself. This could be useful for secure authentication and identity verification without requiring the disclosure of sensitive information.
- Multi-Party Computation: Multi-party computation allows several parties to jointly compute a function without revealing their private inputs to each other. This could be useful for applications like secure voting and auctions.
As the need for secure communication and privacy continues to grow, cryptography will play an increasingly important role in protecting sensitive information. The future of cryptography is likely to involve a combination of these and other new techniques, as researchers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with encryption.
Pros & Cons
Here is a table summarising some of the main pros and cons of using cryptography:
| Pros | Cons |
| Protects sensitive information from unauthorized access and tampering | Requires additional resources and processing power to implement |
| Provides secure communication over untrusted networks | Can be vulnerable to attacks if not implemented properly or if keys are compromised |
| Enables secure data storage and transmission | Can be difficult to manage and secure keys and passwords |
| Can be used for authentication and non-repudiation | Encryption can introduce some level of latency in communication |
| Widely supported by software and hardware | Encryption can be subject to legal restrictions in some countries |
It’s worth noting that the specific pros and cons of using cryptography will depend on the particular implementation and use case.
For example, some encryption methods may be more vulnerable to certain types of attacks than others, and the level of security provided will depend on the strength of the encryption algorithm and the security of the keys used.
Additionally, some types of cryptography may be more suited to certain applications than others, depending on factors like speed, efficiency, and ease of use.
Also read about What Is Software Bug
Frequently Asked Questions :
See cryptographic key. A value used to control cryptographic operations, such as decryption, encryption, signature generation, or signature verification.
First, and most importantly, there are two main types of cryptographic keys: symmetric and asymmetric. The latter always come in mathematically-related pairs consisting of a private key and a public key.
Encryption keys can be generated by the encryption key server, by applications such as Tivoli Storage Manager, or by a utility such as keytool.
Conclusion
A cryptographic key is a numeric value that can be used in a cryptographic system to encrypt or decode data.
It essentially functions as a secret phrase or password that is used to protect data and guarantee that only allowed individuals can access it.
When using symmetric-key cryptography, both parties must have access to the same key since it is used for both encryption and decryption. A public key and a private key are used in public-key cryptography, in contrast.
We hope that this article has helped you to know about Cryptographic Key. If you have any questions, kindly let us know in the comments section.