What Is DDR5 | The latest Generation Of RAM Explained

DDR5
DDR5
Did you know about DDR5? If yes then this article is for you. We will be discussing DDR5. Read on for more.
DDR5 (Double Data Rate 5) is the fifth generation of DDR (Double Data Rate) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) technology. It is the successor to DDR4 and offers several improvements over its predecessor.
DDR5 offers higher memory bandwidth compared to DDR4, with speeds ranging from 3200 MHz to 8400 MHz and a theoretical peak bandwidth of 51.2 GB/s per channel. It achieves this through increased data rates, a wider memory bus (up to 64 bits), and higher bank densities (up to 16 banks per chip).
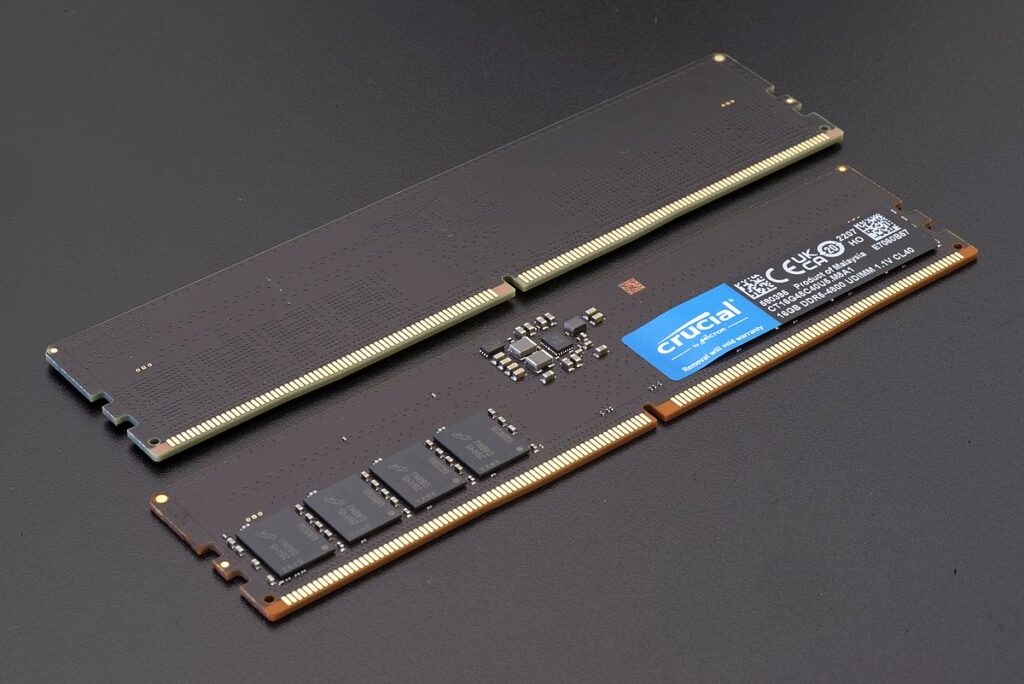
also introduces several new features such as decision feedback equalization (DFE), adaptive voltage scaling, and on-die error correction code (ECC) for improved reliability and power efficiency. DFE helps to mitigate signal degradation caused by high-speed signaling, while adaptive voltage scaling allows for more efficient power consumption by reducing voltage levels when they are not needed. On-die ECC helps to detect and correct errors within the memory without the need for more hardware or software.
memory modules also feature an improved form factor, with a larger number of pins (up to 720) compared to DDR4 (288 pins). This allows for greater memory density and improved thermal performance, which is particularly important in high-performance computing applications.
While DDR5 is not currently supported by mainstream consumer devices, it is expected to become more widely adopted soon, particularly in high-end gaming systems, workstations, and data centers.
Read More Post What Is Cryptographic Key
What is DDR5
DDR5 (Double Data Rate 5) is the latest version of DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory), a type of computer memory that allows for faster data transfer rates between the CPU and RAM. is the successor to DDR4, which was introduced in 2014. offers higher data transfer rates, improved power efficiency, and greater memory density compared to DDR4.
operates at a higher frequency than DDR4, with a target range of 3200 MHz to 8400 MHz. It also uses a 32-bit prefetch buffer, which allows it to transfer 64 bytes of data per clock cycle, compared to DDR4’s 16 bytes per cycle. also uses more advanced error correction techniques, which improves the reliability of the memory.
DDR5 also introduces new features such as decision feedback equalization (DFE) and on-die ECC (Error Correction Code), which helps to improve signal integrity and reduce errors. It also has improved power management features, which reduces power consumption and heat generation.
DDR5 is not backwards compatible with DDR4, meaning that modules cannot be used in DDR4 motherboards, and vice versa. is expected to be adopted by high-end desktops, servers, and gaming systems soon.
Why Do We Need It?
There are several reasons why DDR5 is needed and why it is an important advancement in memory technology:
- Increased Memory Bandwidth: DDR5 offers significantly higher memory bandwidth compared to DDR4. This increased bandwidth is essential for modern computing applications that need high-performance memory to handle large amounts of data in real-time. DDR5’s higher bandwidth makes it possible to run memory-intensive applications more efficiently, improving omit system performance.
- Improved Power Efficiency: DDR5 includes new power management features, such as adaptive voltage scaling, that allow for more efficient power consumption. This is particularly important in data center and high-performance computing environments where power consumption can be a significant cost factor.
- Higher Memory Density: allows for greater memory density, which means more memory can be installed on a single module. This is important for applications that need a large amount of memory, such as databases, virtual machines, and scientific simulations.
- Enhanced Reliability: includes on-die ECC, which helps to detect and correct errors within the memory without the need for more hardware or software. This improves system stability and reduces the risk of data corruption or loss.
- Future-Proofing: is the latest memory technology and is designed to meet the demands of future computing applications. By adopting, system designers can future-proof their systems and ensure they are ready to handle the memory requirements of emerging technologies.
In summary, DDR5 is needed because it offers higher memory bandwidth, improved power efficiency, higher memory density, enhanced reliability, and future-proofing for emerging technologies. These improvements are essential for meeting the demands of modern computing applications.
What Platforms Will DDR5 Work On?
DDR5 memory modules are not backward compatible with previous DDR generations such as DDR4, DDR3, and DDR2. so, memory will only work on platforms that are designed to support DDR5 memory.
Initially, DDR5 memory will be supported by high-end desktop platforms, such as Intel’s Alder Lake-S and AMD’s Ryzen 5000 series processors. Also, server platforms, including AMD’s EPYC Milan and Intel’s Sapphire Rapids, will also support DDR5 memory.
DDR5 memory is expected to become more widely available and supported over time as more platforms are designed to support it. But, it is important to note that DDR5 memory compatibility is not only dependent on the processor but also on the motherboard. So, users must ensure that their motherboard is designed to support DDR5 memory before upgrading.
In summary, DDR5 memory will initially be supported by high-end desktop and server platforms, and support for DDR5 memory is expected to become more widespread over time. But, users must ensure that their system supports DDR5 memory before upgrading as DDR5 memory is not backward compatible with previous DDR generations.
How much memory capacity does DDR5 have?
The capacity of memory depends on the number of memory chips used on a module and the density of the chips. memory chips can range in density from 2 Gb to 32 Gb, which means that DDR5 memory modules can range in capacity from 2 GB to 128 GB.
DDR5 memory modules are typically designed with a capacity of 8 GB, 16 GB, or 32 GB, with some higher-end modules reaching up to 64 GB or more. But, it is important to note that the actual capacity of a DDR5 memory module will depend on the number of memory chips used and the density of those chips.
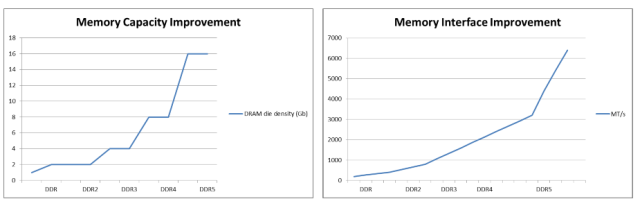
Also to capacity, memory also offers higher memory bandwidth, improved power efficiency, and enhanced reliability compared to DDR4 memory. These improvements make memory an attractive option for high-performance computing applications that need large amounts of memory and fast data transfer rates.
Omit, memory offers a range of capacities depending on the number of memory chips used and their density, with modules ranging from 2 GB to 128 GB or more.
Which processors support DDR5 RAM?
Here is a table summarizing the processors that currently support DDR5 RAM:
| Processor | Type | Release Date | Maximum Memory Capacity | Memory Channels |
| Intel Alder Lake-S | Desktop | 2021 | 128 GB | Dual |
| AMD Ryzen 5000 series | Desktop | 2020 | 128 GB | Dual |
| AMD EPYC Milan | Server | 2021 | 4 TB | Octa |
| Intel Sapphire Rapids | Server | 2023 (Expected) | TBA | TBA |
It’s important to note that is a new technology, and more processors are likely to support it in the future as it becomes more widespread.
Also Read About Know What is Active Directory & How it works?
Frequently Asked Questions :
crucial DDR5 memory is available in 8, 16, and 32GB. Can I use DDR5 RAM on a DDR4 motherboard? No.
With DDR5 memory modules being popular recently these are priced quite a lot higher compared to DDR4 memory modules. You can expect about 50-70% more for a DDR5 memory module. This extra cost is because of the on-module voltage controller, with the global chip shortage inflating the price even more.
If you want the absolute top speed performance, no stuttering issues, lag, or any other graphical or performance hiccups, 32GB might be your ideal of good RAM. Add to that the longevity that 32GB of RAM can provide your hardware, and you may end up saving money by not buying or upgrading new tech.
Conclusion
(Double Data Rate 5) is the fifth generation of DDR (Double Data Rate) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) technology. It is the successor to DDR4 and offers several improvements over its predecessor.
offers higher memory bandwidth compared to DDR4, with speeds ranging from 3200 MHz to 8400 MHz and a theoretical peak bandwidth of 51.2 GB/s per channel.
We trust that you have learned something about DDR5 from this article. Please let us know in the comments area if you have any questions.