What Is A Pixel In Computer Graphics | [2023]

Pixel
Pixel
Did you know about Pixel? If yes then this article is for you. We will be discussing Pixel. Read on for more.
A pixel, short for “picture element,” is the smallest unit of a digital image or graphic that can be displayed and controlled on a screen. It is a tiny square or dot that represents a specific colour or shade in an image. Pixels are arranged in a grid-like pattern on a screen, and the combination of different coloured pixels creates the images we see on digital displays.

The resolution of a screen refers to the number of pixels it can display horizontally and vertically. Higher resolution screens can display more pixels per inch, resulting in a sharper and more detailed image.
What is Pixel
A pixel is the smallest unit of a digital image that can be displayed and controlled on a screen. It is a tiny square or dot that represents a specific color or shade in an image. The term “pixel” is a shortened form of “picture element.”
Pixels are important because they determine the resolution of an image or display. Higher-resolution screens can display more pixels per inch, resulting in a sharper and more detailed image.
Explains Pixel
A pixel, short for “picture element,” is the basic unit of a digital image or graphic. It is a small square or dot that represents a single color or shade in an image.
The combination of different colored pixels creates the images we see on digital displays, including computer monitors, smartphones, and television screens. By changing the color and brightness values of individual pixels, it is possible to create complex images, graphics, and animations.
The resolution of a screen or image refers to the number of pixels it can display horizontally and vertically. A higher resolution screen can display more pixels per inch, resulting in a sharper and more detailed image.
In summary, pixels are the building blocks of digital images, representing individual color and brightness values that combine to create the images we see on our screens.
Read More Posts United States Fed Funds Rate
Screen pixels
Screen pixels are the individual dots of light that make up the images on a digital screen. By changing the color and brightness values of individual pixels, it is possible to create complex images, graphics, and animations.
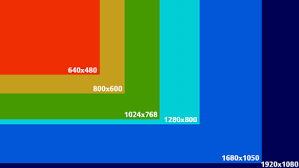
The resolution of a screen refers to the number of pixels it can display horizontally and vertically. A higher-resolution screen can display more pixels per inch, resulting in a sharper and more detailed image.
The size of the pixels on a screen can also affect the quality of the image.
Smaller pixels generally result in a sharper and more detailed image, while larger pixels can lead to a grainy or pixelated image.
THE USE OF THE PIXEL IN GRAPHIC DESIGN
In graphic design, pixels are used as the building blocks of digital images. The color and brightness values of individual pixels are manipulated to create complex images, graphics, and animations. Pixels are used to create both raster graphics and digital photographs, which are composed of pixels arranged in a grid-like pattern.

Designers use pixels to control the resolution and quality of digital images. Higher-resolution images with more pixels per inch generally result in a sharper and more detailed images. But, larger file sizes can also result, which can affect load times and performance.
In summary, pixels are an essential tool for graphic designers, allowing them to create and manipulate digital images with precision and control. By using pixels to control resolution and image quality, designers can optimize their designs for the intended use and create stunning visual effects.
Pixel Features
The features of a pixel can vary depending on the context in which it is used, but some of the key features of a pixel in the context of digital imaging include:
- Color: A pixel can represent a single color, which can be specified using RGB (red-green-blue) or other color models.
- Brightness: A pixel can also represent a specific level of brightness or luminance, which can be used to create shading and other visual effects.
- Size: The size of a pixel can vary depending on the resolution of the image or screen. Higher resolution screens generally have smaller pixels, resulting in a sharper and more detailed image.
- Placement: Each pixel has a specific position in the grid-like pattern that makes up the image or screen.

- Density: The number of pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI) can affect the clarity and quality of the image.
- Transparency: Pixels can also be transparent, allowing other colors or images to show through.
- Interactivity: In some contexts, such as touchscreens or LED displays, pixels can be interactive, responding to touch or other inputs.
Omit, pixels are a fundamental component of digital imaging, allowing for precise control over the colour, brightness, and detail of images and graphics.
Compression
Compression in digital imaging refers to the process of reducing the size of a digital image or file by removing redundant or unnecessary data while preserving as much of the original quality as possible
There are two main types of compression: lossless and lossy.
- Lossless Compression: This type of compression preserves all the original data in the image, while still reducing its file size. Examples of lossless compression formats include PNG and GIF.
- Lossy Compression: This type of compression results in some loss of data and quality in the image. The compression algorithm removes data that is not critical to the image quality, resulting in a smaller file size. The degree of data loss and the resulting image quality can vary depending on the compression algorithm and the degree of compression used. Examples of lossy compression formats include JPEG and MPEG.
Pros & Cons
Sure! Here’s a table outlining the pros and cons of lossless and lossy compression in digital imaging:
| Pros | Cons | |
| Lossless | – Preserves all original data and quality<br>- Reversible | – Typically results in larger file sizes<br>- Limited compression ratio<br>- May not be suitable for all types of images |
| Lossy | – Results in smaller file sizes<br>- Can achieve high compression ratios<br>- Can be suitable for web and digital media | – Results in loss of data and quality<br>- Irreversible<br>- Image quality may not be suitable for all types of images<br>- Compression artifacts may be visible in some cases |
Omit, the choice of compression type depends on the specific needs of the image and the intended use.
Also Read About What Is DDR5
Frequently Asked Questions :
The pixel — a word invented from picture element — is the basic unit of programmable color on a computer display or in a computer image. Think of it as a logical — rather than a physical — unit. Pixels are the smallest unit in a digital display
Image resolution is typically described in PPI, which refers to how many pixels are displayed per inch of an image.
The more pixels per inch, the finer the detail in the print will be and the sharper it will look. Probably the minimum value for reasonable print quality is 180 ppi.
Conclusion
A pixel, often known as a “picture element,” is the smallest unit of a digital image or graphic that may be shown and controlled on a screen.
It is a tiny square or dot that stands in for a certain shade or color in an image. The images we see on digital displays are made up of a collection of variously colored pixels that are placed on a screen in a grid-like arrangement.
We trust that you have learned something about Pixel from this article. Please let us know in the comments area if you have any questions.